"
Disruptive technology that empowers both doctors and patients. "
- Luke Chez

3D Printing: Part of the Future
of Healthcare
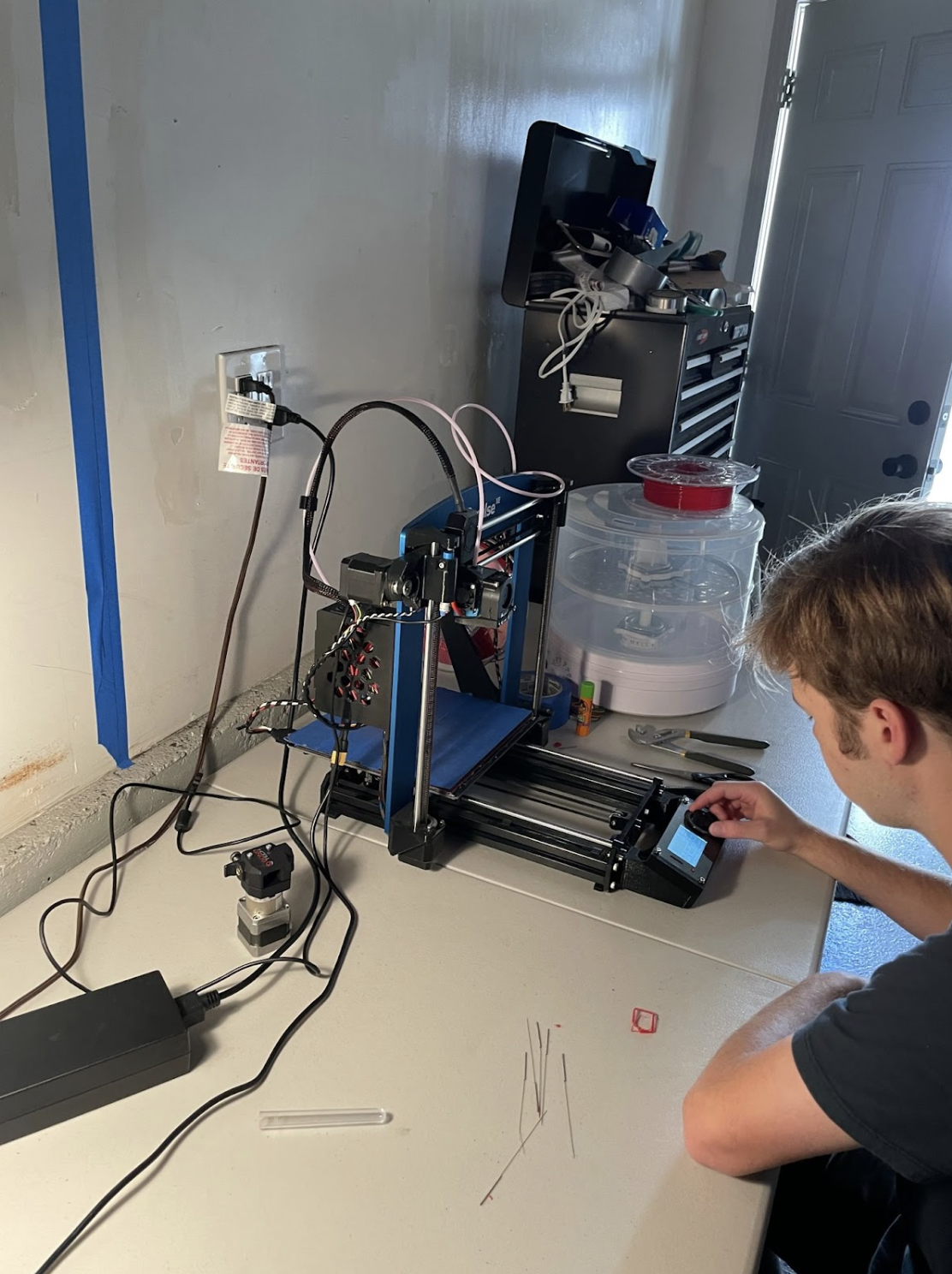
In Practice

The Process
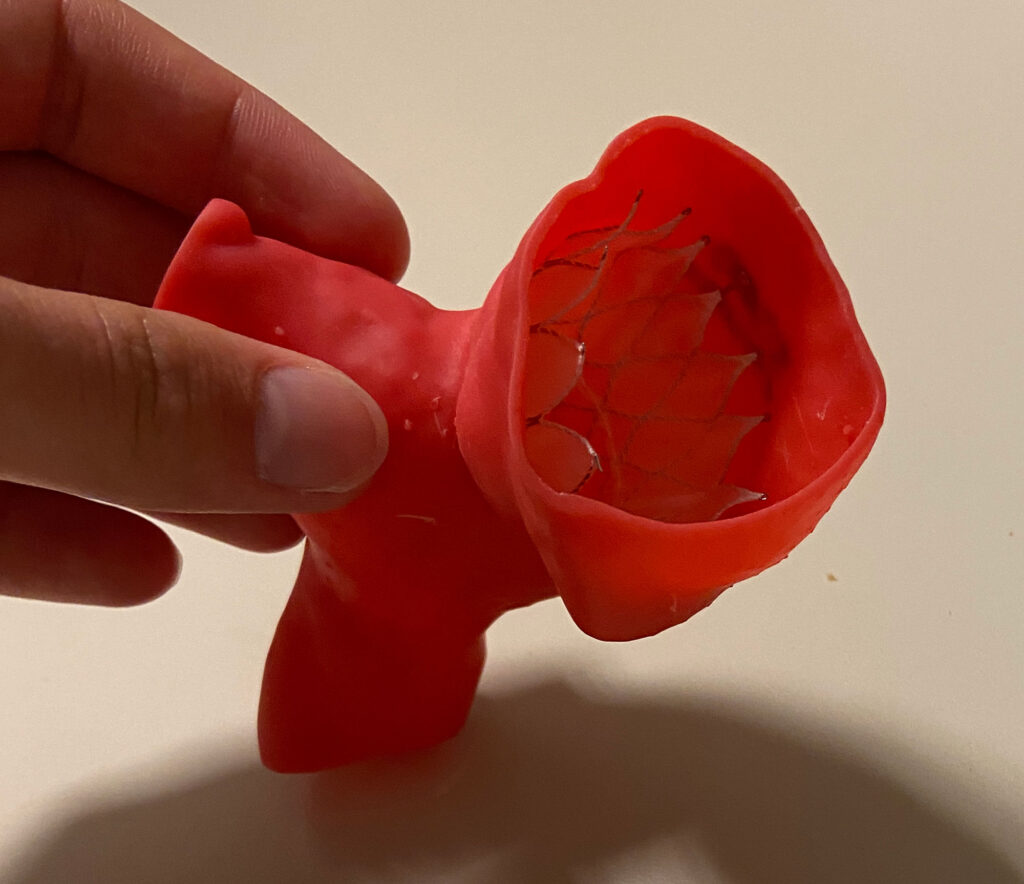
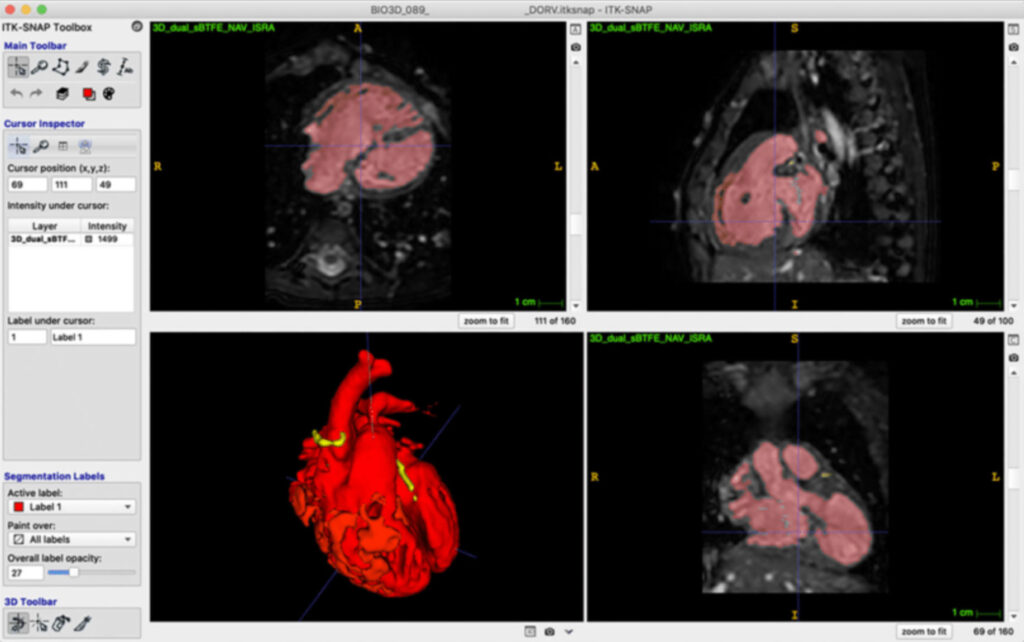
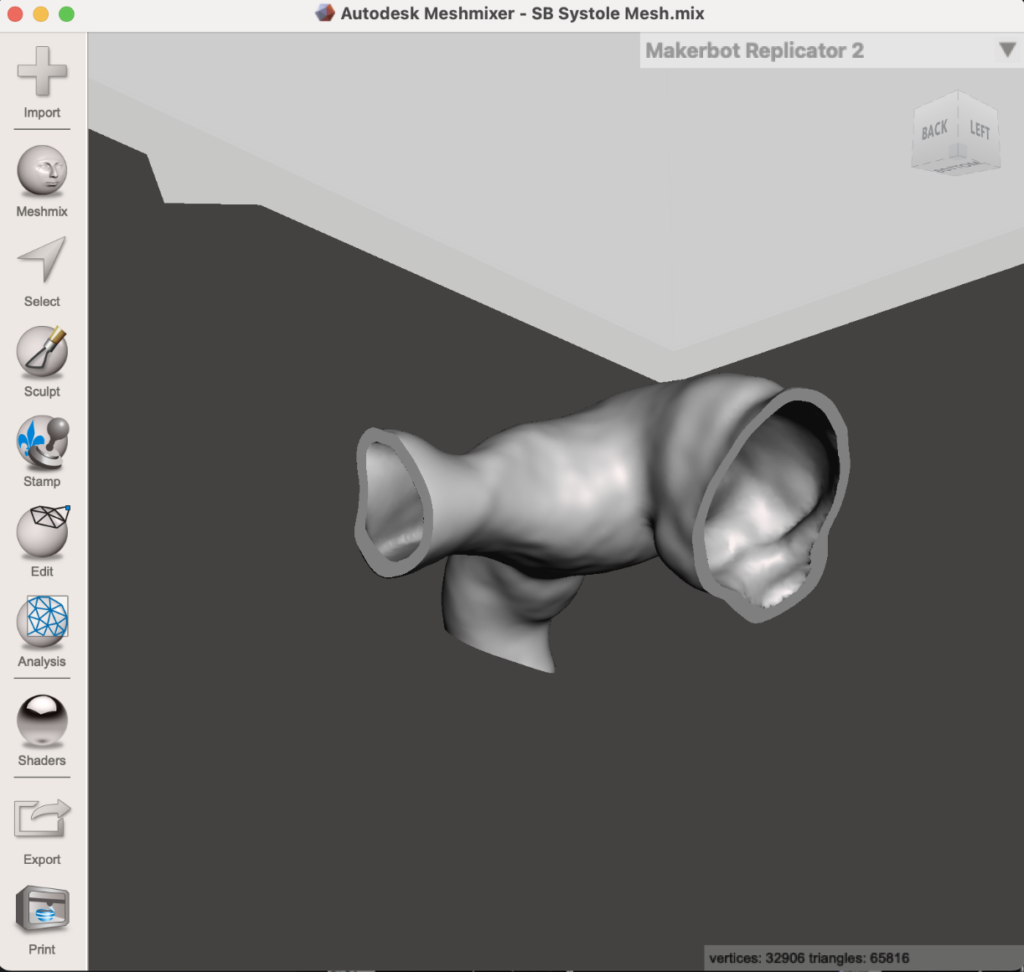

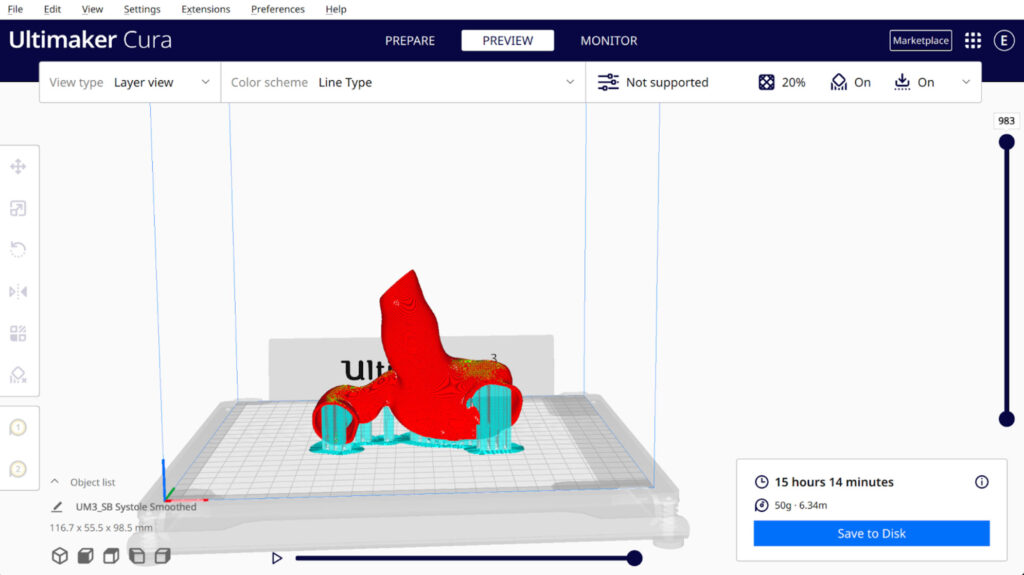
Use Cases for 3D Printing in Healthcare
Preoperative Planning
3D printing is changing preoperative planning which translates into less time spent in the OR, better surgery outcomes for the patients, faster post-op recovery and lower costs for hospitals.
Customized Surgery
Anatomical models that are 3D-printed enable surgeons to plan the operation efficiently and establish better treatment solutions, decrease the operation's duration, and improve research.
Designing Medical Devices
Producing medical device solutions to meet specific criteria, requires extensive time and high costs.
Creating Prostheses
While simple prostheses are available in predefined sizes, customized bionic prostheses cost thousands of dollars.
3D-printed implants
Metal 3D printing enables medical devices designers to produce implants that perform better, match better and last longer.
Streamlining Drug Administration
3D printing can also simplify drug administration with the help of 3D-printed pills.